UV Fading Protection: Glass Options to Safeguard Your Floors and Furnishings
Blog
Anyone who has watched hardwood floors lighten or furniture fabrics lose color over time knows how powerful sunlight can be. The culprit isn’t always heat or visible glare – it’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation, the invisible part of sunlight that gradually fades wood, textiles, and artwork. According to the Canadian Conservation Institute, prolonged UV exposure is one of the main causes of fading and material degradation in indoor environments.
Modern window glass has come a long way in solving this problem. New coatings and laminates can now block nearly all UV rays while keeping your rooms bright and naturally lit. This guide explains how UV fading protection works, the main types of protective glass available, and how to choose the best option for your home.
Understanding UV Fading Protection
UV fading protection refers to glass technologies that block or filter ultraviolet light before it reaches your interior surfaces. Standard clear glass filters out part of the UV spectrum, but enough still gets through to damage colors and finishes over time. The American Museum of Natural History notes that UV radiation is particularly harmful to organic materials such as textiles and paper, which lose color even at low light levels over long exposure periods.
Today’s protective glass options integrate UV-blocking compounds or films directly into the window unit. Some can stop up to 99.9 % of UV rays while maintaining excellent clarity. This balance of transparency and protection allows homeowners to preserve natural daylight without sacrificing the look of their space.
Why It Matters for Your Home
UV protection does more than keep rooms looking new – it helps you save money and preserve the things that make your home comfortable.
- Preserves furnishings: Floors, carpets, and fabrics stay vibrant for years longer when shielded from direct UV exposure.
- Protects valuable items: Photographs, original art, and family keepsakes are safe from irreversible fading.
- Maintains property value: Preventing discoloration of built-in finishes keeps your interior looking fresh and well cared for.
- Improves efficiency: Many UV-protective options, such as Low-E glass, also improve insulation and reduce heating and cooling costs.
Comparing UV Protection Options
Homeowners can achieve UV fading protection through several different window solutions. The right choice depends on your budget, project type, and how much light control you need. As explained by the Whole Building Design Guide, modern window films reduce interior fading by blocking a substantial portion of UV rays, protecting furnishings without significantly altering visible light transmission.
| Parameter | Low-E Glass Windows | Laminated Glass Windows | UV-Blocking Window Film |
| UV Blockage | 75-95% | Up to 99.9% | Up to 99.9% |
| Installation | Full window replacement | Full window replacement | Applied to existing glass |
| Cost | High | High | Low to Medium |
| Key Benefits | Energy savings, UV reduction | Safety, sound control, UV block | Low cost, easy retrofit |
Choosing the Right Option
Start by thinking about your project goals and the level of protection required.
- For new builds or replacements: Select windows with Low-E or laminated glass. These provide integrated, long-term UV defense plus energy savings.
- For existing windows: A professional-grade UV film can offer outstanding protection at a fraction of the cost and without major renovation.
- For maximum defense: Laminated glass or top-tier films that block 99.9 % of UV rays are ideal in rooms with valuable artwork or strong sunlight exposure.
- For additional needs: If noise reduction or impact resistance are priorities, laminated glass provides both.

Mistakes to Avoid
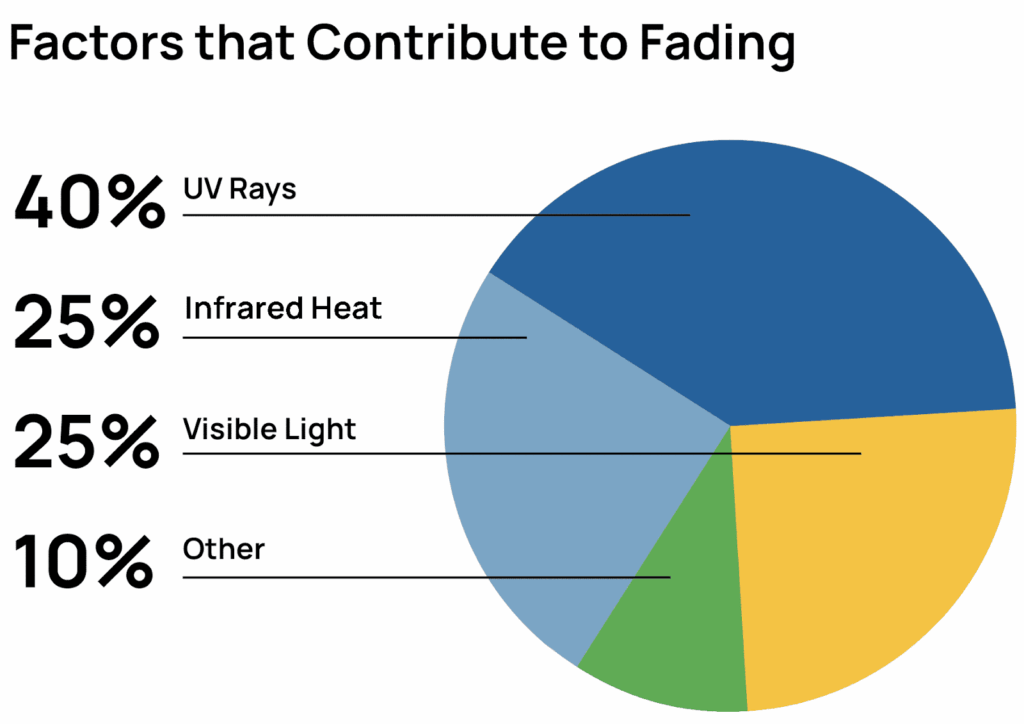
- Relying on UV protection alone. UV radiation causes around 40 % of fading, but visible light and heat each contribute roughly a quarter. Managing all three factors gives the best results.
- Ignoring light control. Combine UV glass with interior shades or blinds to reduce visible light exposure during bright hours.
- Overlooking heat gain. Choose windows with a low Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) to limit temperature-related fading.
- Skipping certification checks. Always confirm that products carry verified performance ratings from recognized testing organizations.
Film or Full Replacement?
For many homeowners, the main question is whether to replace windows or simply apply film. Full replacements deliver the strongest and most permanent results but require a larger investment.
High-quality films, on the other hand, can block nearly all UV rays and even reduce heat gain. They are an excellent option for sound windows that don’t need replacement and can often be installed in a single day. Combining a UV film with existing Low-E glass enhances protection without altering the appearance of your home.
Standards and Ratings
When reviewing window products, check the certification labels for UV performance and overall energy efficiency. In North America, ratings from the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) indicate tested performance for U-Factor, Solar Heat Gain Coefficient, and Visible Transmittance. These values help you compare options and choose a product that aligns with both your protection and energy goals. The Efficient Windows Collaborative reports that Low-E coatings can block up to 75 % of UV radiation, while UV-absorbing laminated materials can reach 99 % blockage – offering reliable long-term protection for floors, furniture, and artwork.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What should I consider when choosing UV fading protection?
Consider the value of the items you are protecting, your budget, and whether you are replacing windows or upgrading existing ones. Remember that UV rays are only one cause of fading; you must also manage visible light and heat.
2. How do I choose the best glass option?
For the best all-in-one package (energy savings, UV protection), choose a high-performance Low-E glass. For maximum UV protection plus security and noise reduction, choose laminated glass. For a cost-effective upgrade to existing windows, choose a 99.9% UV-blocking film.
3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of UV protection?
The main advantage is the preservation of your floors, furniture, and artwork, saving you money and protecting valuables. There are no significant disadvantages, though some solutions have a high upfront cost (new windows) or may not block 100% of fading causes (as heat and visible light also play a role).
Conclusion
UV fading protection is an easy step that pays off over time. Whether through advanced Low-E or laminated glass or by adding a UV-blocking film, these technologies protect the colors and materials that make your home inviting. By managing not only UV rays but also light and heat, you can preserve your floors, furniture, and artwork for many years while keeping your home bright, efficient, and comfortable.
For more general information on the properties of different glass types, you can visit authoritative sources such as Wikipedia’s page on Laminated Glass.
Recent Posts
- Care and Cleaning Guide for Black and Dark-Colored Window Frames
- Child-Safe Venting Strategies for Nurseries and Kids’ Rooms
- Lead-Time and Supply-Chain Tips: Ordering Windows Without Delaying Your Build
- ROI of Window Replacement in 2026: Payback, Comfort, and Resale Value
- Big Openings on a Budget: Combining Units or Choosing Custom Spans


